We are talking about the creation of articulated construction dump trucks based on the use of units and assemblies of serially produced rigid-frame models, which will increase production volumes and reduce the cost of production of this type of equipment.
This year, within the SPbGASU grant for the implementation of scientific research by scientific and pedagogical workers in the scientific direction "Automobile and Road Complex and Intelligent Transport Systems", Viktor Dobromirov, DSc in Engineering, Professor and Ulyana Meike, PhD of Engineering Sciences with the active participation of the PhD student at the SPbGASU Department of Land Transport and Technological Machines (LTTM) Kirill Fomin, who performed under his dissertation research, have completed R&D No. 7-NPR-24 "Study of the load of unified units of transmissions of wheeled road construction machines".
The authors of the research work considered a solution to one of the aspects of creating articulated vehicles - the use in their design of serially produced units and transmission assemblies from heavy-duty dump trucks of traditional rigid frame design. To recall, an articulated vehicle usually consists of two rigid sections, articulated with each other. The rotation of such machines is carried out not by means of the front steered wheels, but by mutual folding of the frame sections in the horizontal plane using hydraulic power cylinders. This principle of rotation allows the use in the design of the machine of wheels with tires of a significantly larger diameter and width in comparison with rigid frame models. This provides an undeniable advantage of articulated two-link machines over rigid frame ones in terms of cross-country ability and maneuverability, which is important for road construction production.
The attention of researchers to this type of transport is due to several reasons. Firstly, the domestic road construction industry is experiencing a shortage of heavy-duty dump trucks - earthmovers based on wheeled chassis with an articulated frame. The shortage is caused by the high cost of acquisition and restrictions on the supply of foreign models due to the sanctions policy of unfriendly manufacturing countries. As the experience of some domestic manufacturers has shown, the development of such machines in Russia in the most popular class of 25 tons of load capacity is also limited by the high cost of their creation on the basis of special production.
Secondly, there is a growing demand for dump trucks of this type, especially for the implementation of large-scale road construction projects in the off-road conditions of Siberia, the Far East and the Arctic. Therefore, the launch of domestic production of articulated construction dump trucks has become especially relevant.
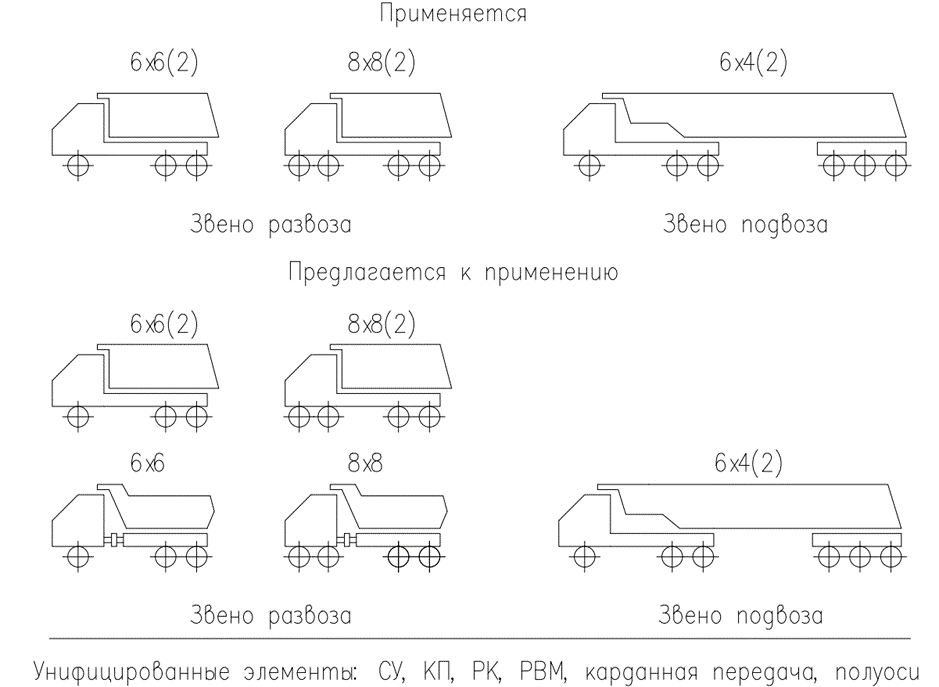
The authors of the study found that it is possible to increase the output and at the same time reduce the cost of production of domestic articulated dump trucks if they are created as part of highly unified families of machines based on serially produced rigid-frame models at enterprises of the automotive industry for the production of trucks. In this regard, the scientists proposed to include in the general nomenclature of produced heavy-duty construction dump trucks-earth movers machines of the 6x6 and 8x8 type with a two-link articulated frame and the wide use in their design of units and assemblies unified with rigid-frame machines, primarily in terms of elements of the drive of the chassis (Fig. 1).
In 2017, the largest domestic automobile concern KAMAZ, as part of the implementation of a similar concept, presented its first articulated general-purpose vehicle of the 6x6 type with a load capacity of 13.0 tons - KAMAZ-6345-3101, designed for work in Arctic conditions. The vehicle with a gross weight of 30 tons is equipped with a KAMAZ-740.37 400 power plant (V8, 11.76 l) with a capacity of 400 hp. The powertrain includes a single-plate diaphragm clutch MFZ 430, a mechanical 16-speed gearbox ZF 16S 1822, a two-speed transfer case "KAMAZ-633 1800020" with torque distribution between the front axle and the rear bogie in the ratio of 27.5%: 72.5%, equipped with a locking center differential, and drive axles with wheel reducers borrowed from the "KAMAZ-6520".
In 2019, an articulated model of the KAMAZ-6355 8x8 type with an increased load capacity of up to 16 tons was created. The model is equipped with a KAMAZ R6 910.12.12 engine with a capacity of 450 hp, an Allison 4500 gearbox with 6 speeds. The transfer case is unified with the KAMAZ-6345 gearbox (6x6).
Both vehicles are equipped with 710/70 R38 / 1000x50R25 SB1 tires with a permissible radial load of 5 t and a maximum speed of 65 km/h on asphalt and 50 km/h on dirt roads.
As part of the study in the interests of road construction, the researchers assessed the possibilities of improving the design of the articulated model of the KAMAZ 6x6 by increasing its load capacity to 25 tons and installing dump truck equipment on it. They also compared this design with a serial rigid-frame model of similar load capacity in terms of the main operational properties. Particular attention was paid to the reliability of the proposed standardized units and assemblies. The most critical standardized elements in this case are the transmission units and assemblies. In this regard, it became necessary to compare their loads in the basic rigid-frame and newly created articulated machines during movement, accompanied by the emergence of significant circulating moments in the closed (blocked) drive circuits of the drive axles.
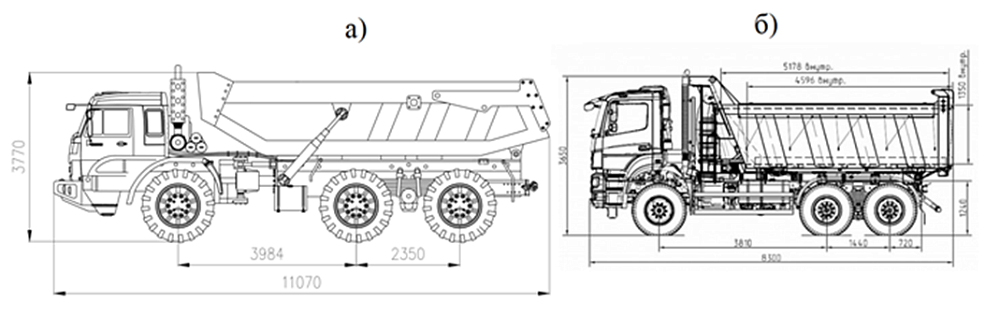
Considering the limited scientific research in this area, scientists have developed a method for calculating the load on the locked drives of the chassis of wheeled multi-drive road construction machines. In this way, they obtained the calculated values of torques loading the axles of the locked transmission circuits of the basic rigid-frame and proposed articulated machines when maneuvering in the limited space of a road embankment, overcoming single obstacles of various geometric profiles on the way - ditches, ruts, scarps, steep short climbs and descents, and moving on soils with low bearing capacity. The developed conceptual appearance of the articulated machine and the general appearance of its serial rigid-frame analogue "KAMAZ 65802" are shown in Fig. 2.
The main performance indicators for the articulated vehicle were predicted during the study, and for its serial analogue were taken from technical literature. Calculations showed that the loads in the wheel drive of the articulated vehicle increase by no more than 20% compared to the rigid frame. However, for the vast majority of serial structural elements of the drive, such an excess does not cause stresses exceeding the permissible ones.
The obtained results provide grounds to consider the concept of creating articulated construction wheeled dump trucks with a load capacity of 25 tons as part of highly unified families of dump trucks, proposed in the research work, as justified and feasible.